Quick Start
This chapter serves to guide you through the quick and convenient deployment of Synergos locally in various configurations, and point to the available run examples for you to get an introductory understanding to using the system.
Set up basic requirements
Pre-requisites to run Synergos in this guide are:
- Bash Command Line / Terminal (CLI)
- Docker
- Docker Compose
- Conda Environment with Python 3.7 and above
Pull repository and install Synergos
In your CLI, run the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/aimakerspace/synergos_simulator.git
# Navigate into the repository
cd ./synergos_simulator
# Checkout to stable tag
git checkout tags/v0.1.0
# Update Submodule
git submodule update --init --recursive
git submodule update --recursive --remote
# Setup virtual environment
conda env create --name <synergos_env> --file=environment.yml
# Install in development mode
pip install -e ./synergos
Setting up the environment
Synergos comes in 3 main configurations. Depending on your choice of Synergos configuration, you can skip to the respective guides below:
Synergos Basic
# Start Synergos Basic grid
docker-compose -f docker-compose-synbasic.yml up --build
If you had previously built the images or run the same command above on the current version, you may omit the
--buildflag. The omission allows you to skip building the requisite images from scratch again.
On running Docker Compose, you have set up Synergos with the following configuration and network of components locally.
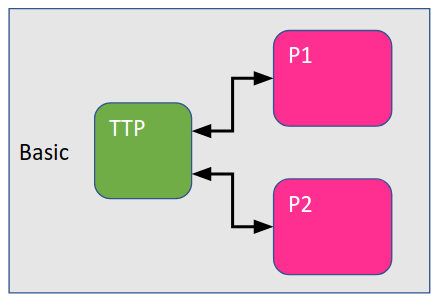
The host IP and ports for each relevant component containers is shown in the table below. This information is important when you are required to register the components, if you run Synergos with Synergos Dashboard UI.
| Name | Service | Component | Host | Port(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
synb_ttp |
TTP | synergos_ttp | 172.18.0.2 |
Orchestrator Port: 5000 |
synb_worker_1 |
Participant 1 Node | synergos_worker | 172.18.0.3 |
Command Port: 5001Data Port: 8021 |
synb_worker_2 |
Participant 2 Node | synergos_worker | 172.18.0.4 |
Command Port: 5002Data Port: 8022 |
Synergos Plus
# Start Synergos Plus grid
docker-compose -f docker-compose-synplus.yml up --build
If you had previously built the images or run the same command above on the current version, you may omit the
--buildflag. The omission allows you to skip building the requisite images from scratch again.
On running Docker Compose, you have set up Synergos with the following configuration and network of components locally.
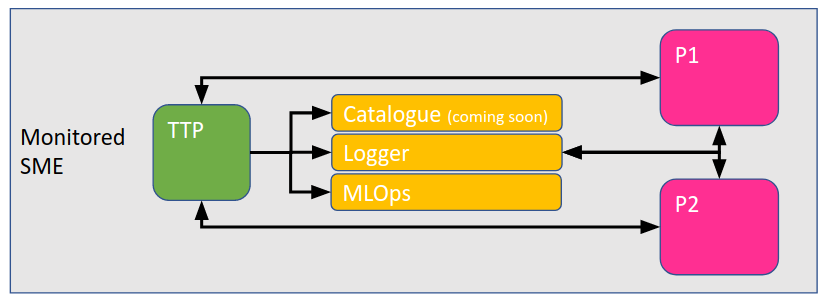
The host IP and ports for each relevant component containers is shown in the table below. This information is important when you are required to register the components, if you run Synergos with Synergos Dashboard UI.
| Name | Service | Component | Host | Port(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
synp_ttp |
TTP | synergos_ttp | 172.19.0.2 |
Orchestrator Port: 5000 |
synp_worker_1 |
Participant 1 Node | synergos_worker | 172.19.0.3 |
Command Port: 5001Data Port: 8021 |
synp_worker_2 |
Participant 2 Node | synergos_worker | 172.19.0.4 |
Command Port: 5002Data Port: 8022 |
synp_logger |
Logger | synergos_logger | 172.19.0.10 |
Server Port: 9000UI Port: 9000Sysmetrics Port: 9100Director Port: 9200TTP Port: 9300Worker Port: 9400 |
synp_mlops |
Federated MLOps | synergos_mlops | 172.19.0.11 |
Server Port: 5500UI Port: 5500 |
Synergos Cluster
# Start Synergos Cluster grid
docker-compose -f docker-compose-syncluster.yml up --build
If you had previously built the images or run the same command above on the current version, you may omit the
--buildflag. The omission allows you to skip building the requisite images from scratch again.
On running Docker Compose, you have set up Synergos with the following configuration and network of components locally.
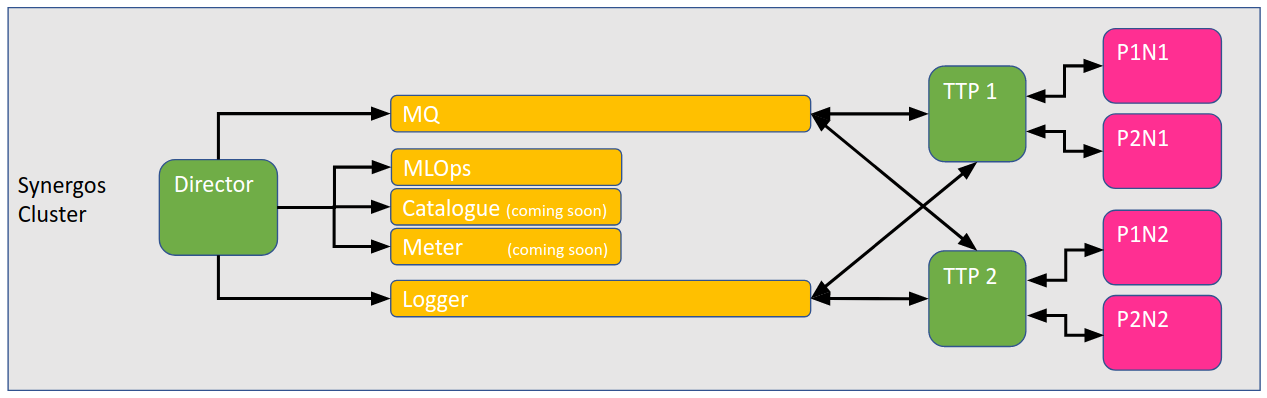
The host IP and ports for each relevant component containers is shown in the table below. This information is important when you are required to register the components, if you run Synergos with Synergos Dashboard UI.
| Name | Service | Component | Host | Port(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
sync_director |
Director | synergos_director | 172.20.0.2 |
Orchestrator Port: 5000 |
sync_ttp_1 |
TTP 1 | synergos_ttp | 172.20.0.3 |
- |
sync_worker_1_n1 |
Participant 1 Node 1 | synergos_worker | 172.20.0.4 |
Command Port: 5001Data Port: 8021 |
sync_worker_2_n1 |
Participant 2 Node 1 | synergos_worker | 172.20.0.5 |
Command Port: 5002Data Port: 8022 |
sync_ttp_2 |
TTP 2 | synergos_ttp | 172.20.0.6 |
- |
sync_worker_1_n2 |
Participant 1 Node 2 | synergos_worker | 172.20.0.7 |
Command Port: 5003Data Port: 8023 |
sync_worker_2_n2 |
Participant 2 Node 2 | synergos_worker | 172.20.0.8 |
Command Port: 5004Data Port: 8024 |
sync_logger |
Logger | synergos_logger | 172.20.0.14 |
Server Port: 9000UI Port: 9000Sysmetrics Port: 9100Director Port: 9200TTP Port: 9300Worker Port: 9400 |
sync_mlops |
Federated MLOps | synergos_mlops | 172.20.0.15 |
Server Port: 5500UI Port: 5500 |
sync_mq |
Message Queue | synergos_manager | 172.20.0.16 |
Server Port: 5672UI Port: 15672 |
Train a Federated Learning Model and Run Inference
Synergos allows you to interact with the Federated Grid to run training and inference, either through Jupyter Notebook or the Synergos Dashboard UI.
Jupyter Notebook
To experience running on Jupyter Notebook, you may access one of the Notebook of one of the many example datasets within the Dataset directory of the repository. Depending on the Synergos configuration you have chosen to run, select the respective Notebook with the correct suffix in each dataset. The configuration to suffix mapping follows:
- Synergos Basic :
_synbasic - Synergos Plus:
_synplus - Synergos Cluster:
_syncluster
Ensure you are using the Conda environment where you had previously installed the Synergos Driver python package.
Synergos Dashboard UI
It is recommended that you first understand the general flow of setting up and running the orchestration of Federated Training on Synergos Dasboard UI here.
To access the Synergos Dashboard UI, go to localhost:4000 in your browser.
The example datasets are available within the Datasets directory in the Synergos Simulator repository you have cloned.
Restart Synergos State
If you want to change the dataset example used, you can restart the state of the grid without terminating and restarting the configured components. This is done by clearing all meta-data and outputs from the previous runs on the grid's volume. To do this, run the following command in your CLI:
# Navigate into the repository
cd ./synergos_simulator
# Grant permission to run cleanup.sh
chmod +x ./cleanup.sh
# Perform cleanup!
./cleanup.sh
If you want to change the Synergos configuration, you will have to terminate and clean up the Synergos Grid entirely.
Terminate and Clean Up the Synergos Grid
To terminate the entire grid and clean up any generated outputs or meta-data, run the following command in your CLI.
# Navigate into the repository
cd ./synergos_simulator
# Grant permission to run cleanup.sh
chmod +x ./cleanup.sh
# Perform cleanup!
./cleanup.sh
# Terminate grid
docker-compose down